We take for granted that the Christmas Season entails children are home from school, festive meals are being prepared, airports are crowded as people rush home to their families and parties are in full swing, all in anticipation of the jolly old elf Santa Claus’s arrival. Not many people realize though that all of those traditions have their origins in the Civil War.
Lloyd W Klein explains.
The religious nature of the holiday season upon us aside, this time of year has been a time of celebration and gift giving for centuries. The Twelve Days of Christmas and many other traditional songs, as well as Dickens’s Christmas Carol, show that this is a celebration time that goes way back in the European culture. This week we are going to trace how the Civil War led to the making of Christmas as a secular, national holiday.
Unsurprisingly, the story is at base a political one. On Christmas Day 1861, President Lincoln chose to host a party at the White House. It was a crucial political moment because Mr Lincoln had a brewing international crisis that he had to stop before it got out of hand.
On Christmas Day 1862, the country was in a national panic. Setbacks in the war had made it anything but a happy season. On this day, Mr and Mrs Lincoln did something that seems so much a part of the responsibility of the POTUS on this holiday that its astounding that it hasn’t always been traditional. And on Christmas in 1863, the Lincoln’s made yet another gesture of good will to the soldiers in the field.
In 1861 President Lincoln sought to limit an international crisis by throwing a Christmas Party at the White House. The Trent Affair had led to the capture of the appointed Confederate representatives to Britain and France, John Slidell and James Murray Mason. War clouds had started to collect as the British Prime Minister insisted that the US had no right to capture these men on open seas. The capture occurred on November 8 and had become an international scandal after November 18. By Christmastime, there were rumors of British preparations for war and also significant diplomatic efforts were in progress. There were rumors of an invasion from Canada .So, there was a lot for Lincoln to “soft shoe” that day.
In 1862, the Lincoln Family began a tradition to counter the public effects of The Battle of Fredericksburg, which had been a military disaster that spawned a political and public relations catastrophe. “What will the country say?” Lincoln asked. But the POTUS was a political mastermind, and he turned crisis into opportunity, The Lincolns pointedly went the various hospitals around Washington and visited and spoke with the wounded. No president had ever done this before. It showed that Lincoln the commander in chief was a sensitive leader who felt the people’s pain.
The hospital visits were so popular, and so necessary, that Lincoln continued them. He brought his son Tad with him on many such days. Tad was deeply moved by the soldiers. So on Xmas 1863, wounded soldiers received gifts of books and clothing from the White House, with a covering note that said, “From Tad Lincoln”.
And in 1864, General Sherman telegrammed Lincoln on December 22, 1864 announcing the capture of Savanah. By 1865, as the image above shows, Christmas was a celebration of victory in. the war.
The soldiers on the battlefield were far away from home, many had never been outside their county in their lives let alone their state. Union soldiers used salt pork and hardtack to decorate Christmas trees. Others were treated to special meals; a captain from Massachusetts treated his soldiers to foods such as turkey, oysters, pies, and apples; Singing carols was popular, ones that remain popular today, but Christmas cards would not become popular until the 1870s.
When we fly or drive home to Grandmothers House for Christmas, the origin of that tradition is the Civil War Fathers on both sides of the war were often given furloughs to return home for the holiday.
Christmas originates with a significant religious meaning and yet it has become secular in its celebration. Almost no one knows that this trend began in the Civil War. And even more surprising to many, without Thomas Nast, Christmas as we know it probably wouldn’t exist. But Nast wasn’t interested so much in Christmas. He was interested in a much bigger issue.
Nast was a cartoonist for Harper’s Weekly during the Civil War. If Nast wasn’t so interested in Christmas, why the recurrent theme? The 2 Nast cartoons depict Christmas experiences during the war. Identify the subjects of each and what was groundbreaking about them.
The fact is that Nast was a first class political cartoonist who was a Union sympathizing propagandist using Christmas to draw on the emotions of the season to bring the country together.
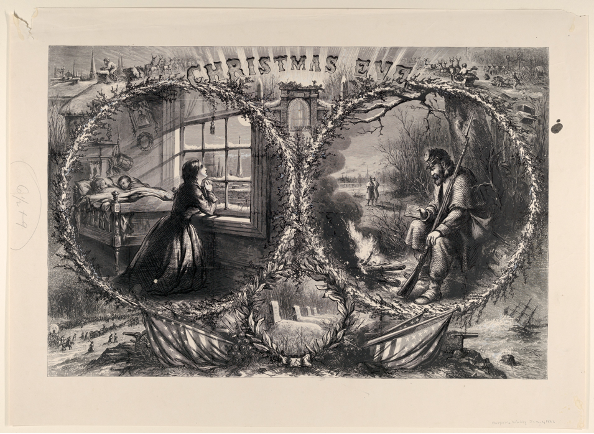
In the top cartoon, "Christmas Eve" (1862), a wreath frames a scene of a soldier's praying wife and sleeping children at home; a second wreath frames the soldier seated by a campfire, gazing longingly at small pictures of his loved ones.
Another illustration features Santa in his sleigh, then going down a chimney, in the top left of the cartoon. Somber scenes below remind of a grimmer reality--an army marching through snow and a row of frozen graves that refers to the Union's recent failure to take Fredericksburg. But there is hope: Santa is coming!
the January 3, 1863 issue of Harper's Weekly, Nast has an early caricature of Santa dressed in an American flag, with a puppet with the name "Jeff" written on it, Nast was inspired by the Belsnickel, part of the folklore in southwestern Germany, You’ll notice his sleigh is drawn by 2 scrawny reindeer.
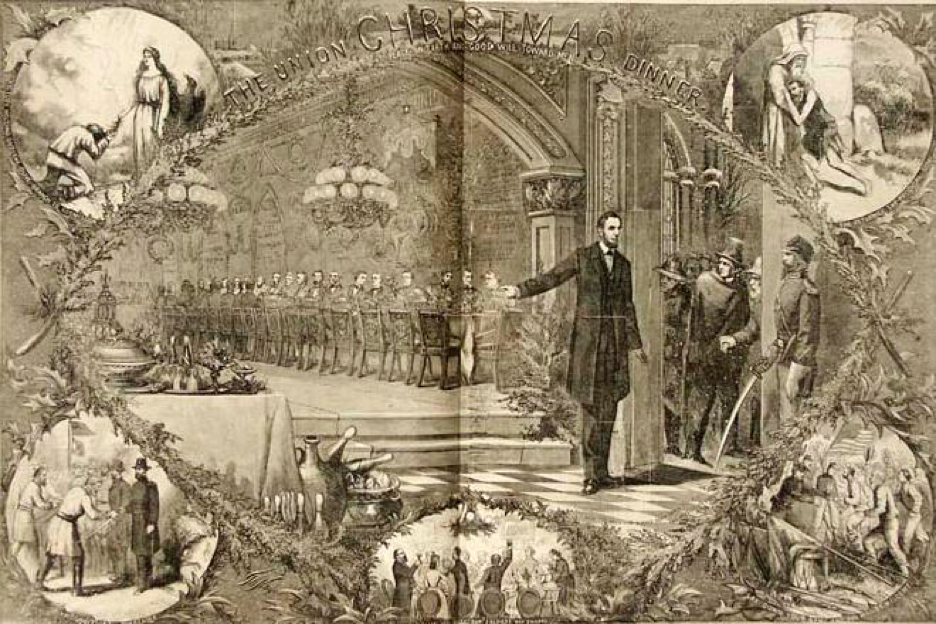
Nast’s 1864 Christmas cartoon in Harper’s. You can clearly see Lincoln beckoning men outside the door into the Christmas feast. But once again, he is making a political point. . Lincoln is seen ushering in the Confederates to re-join the US in a celebratory setting. of a holiday held in common. It is, of course, pure propaganda, but consistent with the war goal of reunification.
Nast’s Christmas cartoons were so successful that he essentially created much of the holiday we know. Nast was not the only one to use Christmas as a propaganda tool. On the Union side, The New York Herald also engaged in propaganda. One illustration published in the paper included Santa Claus fuming that he could not reach southern children, due to the northern blockade. On the Confederate side, The Richmond Examiner described Santa to its young readers as "a Dutch toy monger" who was a New York/New England "scrub" and Hottentot that had nothing to do with traditional Virginian celebrations of Christmas. Nast had successfully made Christmas a Union holiday, and that is propaganda at a very high level.
“In these two drawings, Christmas became a Union holiday and Santa a Union local deity,” writes Adam Gopnik in a 1997 issue of the New Yorker. “It gave Christmas to the North—gave to the Union cause an aura of domestic sentiment, and even sentimentality.” Nast’s 1863 Christmas cartoon showed the couple shown in 1862 reunited.
Use of a Santa-like figure for propaganda purposes would eventually lead after the war to the elf myth of the jolly old Saint Nick. Between 1862 and 1886, Nast created thirty-three Santa Claus drawings. The iconic version of Santa Claus as a jolly man in red with a white beard and a sack of toys was immortalized in 1881, depicted by Nast in the cartoon attached, But he also gave the definitive appearance to Uncle Sam, America personified. Notice how they both have white beards, but one is tall and thin and the other short and plump. Nast didn’t invent Uncle Sam, as many people believe, but he did standardize his appearance and affect. Santa Claus derives from Sinterklaas, the Dutch rendering of St Nicholas, which was popularized in the 1823 poem “A Visit From St. Nicholas”.
DGCC: Notice that the Santa in the 1881 cartoon is smoking an old-style Dutch clay pipe and has a Civil War saber (?toy) hanging from his waistband. He is carrying a knapsack on his back, not filled with clothes and war supplies anymore, but with toys. These details are deliberate; Nast is immortalizing a new personification: the former Union soldier is now older, happily smoking an old pipe, and raising a family 16 years after the war’s end. But the old soldier is still in him. Nast knew his business.
It was also Thomas Nast who decided that Santa and his reindeer lived at the North Pole. After the war Nast purposely made the North Pole the home of Saint Nick so that no one else could use him for nationalistic propaganda like Nast himself did.
It’s hard to imagine today, but Christmas was not always considered a “national” holiday.
Because of the recognition that soldiers on both sides of the war, and of all religious backgrounds, found end of the year celebrations as fostering community and country, that view began to change. Politicians started to recognize in the post war period that if they wanted to bring the country together and heal wounds, Xmas was a natural solution.
Puritans and Lutherans viewed non-sectarian celebrations of Christmas during the war as sacrilegious. They believed the day should be dedicated to fasting and prayer, and looked askance at such practices. In Massachusetts, such parties were considered a waste of money and could be fined.
The legal recognition of Christmas as a national holiday occurred when Representative Burton Chauncey Cook of Illinois introduced a bill in the U.S. Congress after the war. It passed in both houses of Congress, and President Ulysses S. Grant signed it on June 28, 1870. On June 26, 1870, Congress — led by Northern legislators — passed a law that made Christmas (along with New Year’s Day, Independence Day, and Thanksgiving) a federal holiday for federal employees in Washington, D.C. This was later extended nationwide. Ulysses S. Grant signed the law, partly as a gesture of reconciliation between North and South during Reconstruction.
The site has been offering a wide variety of high-quality, free history content since 2012. If you’d like to say ‘thank you’ and help us with site running costs, please consider donating here.